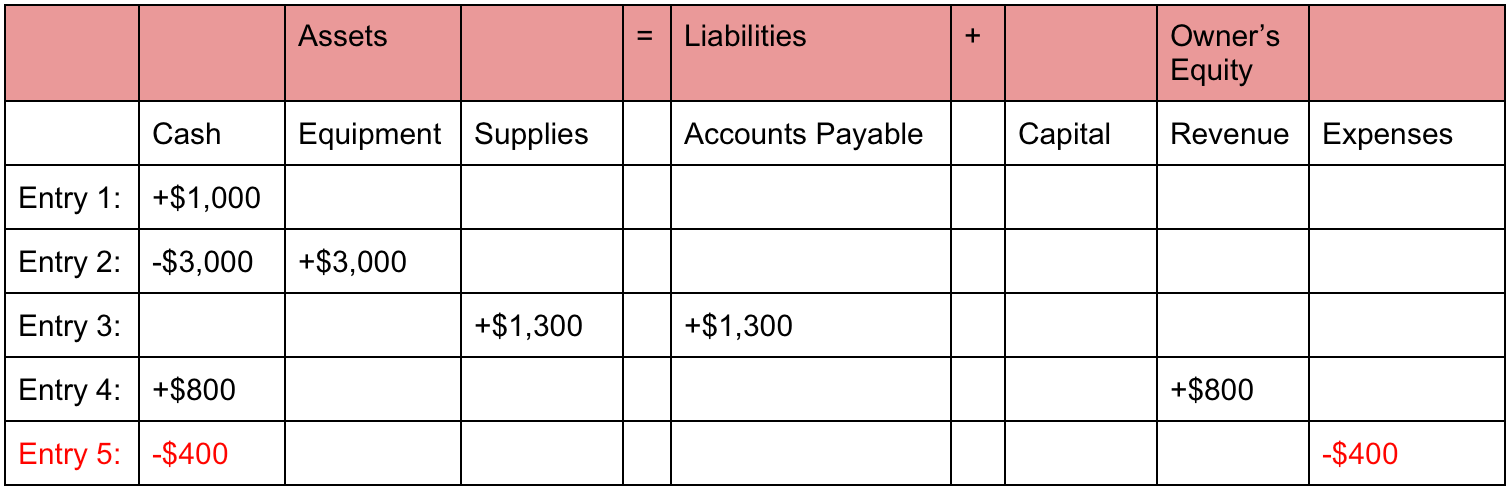
After saving up money for a year, Ted decides it is time to officially start his business. He forms Speakers, Inc. and contributes $100,000 to the company in exchange for all of its best accounting software for advertising agencies newly issued shares. This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount. We know that every business holds some properties known as assets.
Single-entry vs. double-entry bookkeeping system
The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. As a core concept in modern accounting, this provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle.
Components of the Basic Accounting Equation
This post focuses on answering a popular question – What is the accounting equation? We’ll start off with the equation itself and then dive in to the details of each variable. This formula represents the accounting identity, which must always be true for all entities regardless of their business activity. And we find that the numbers balance, meaning Apple accurately reported its transactions and its double-entry system is working. However, equity can also be thought of as investments into the company either by founders, owners, public shareholders, or by customers buying products leading to higher revenue.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
As a side note, this latter interpretation of the accounting equation is used more so in Finance vis-a-vis the former interpretation. It can also cause problems with taxes and audits, as well as customers who may suspect fraud or mishandling of funds as a result of an unbalanced equation. This arrangement can be ideal for sole proprietorships (usually unincorporated businesses owned by one person) in which there is no legal distinction between the owner and the business. For example, John Smith may own a landscaping company called John Smith’s Landscaping, where he performs most — if not all — the jobs. Plus, errors are more likely to occur and be missed with single-entry accounting, whereas double-entry accounting provides checks and balances that catch clerical errors and fraud. Almost all businesses use the double-entry accounting system because, truthfully, single-entry is outdated at this point.
Owners’ Equity
The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20. This transaction would reduce cash by $9,500 and accounts payable by $10,000. The difference of $500 in the cash discount would be added to the owner’s equity. On 12 January, Sam Enterprises pays $10,000 cash to its accounts payable. This transaction would reduce an asset (cash) and a liability (accounts payable).
The third part of the accounting equation is shareholder equity. The revenue a company shareholder can claim after debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity. $10,000 of cash (asset) will be received from the bank but the business must also record an equal amount representing the fact that the loan (liability) will eventually need to be repaid.
- Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, bank loans, and taxes.
- In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity.
- For instance, inventory is very liquid — the company can quickly sell it for money.
- Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
At this point, let’s consider another example and see how various transactions affect the amounts of the elements in the accounting equation. The Accounting Equation is a vital formula to understand and consider when it comes to the financial health of your business. The accounting equation is a factor in almost every aspect of your business accounting. The accounting equation states that the amount of assets must be equal to liabilities plus shareholder or owner equity. There are different categories of business assets including long-term assets, capital assets, investments and tangible assets. They were acquired by borrowing money from lenders, receiving cash from owners and shareholders or offering goods or services.
Liabilities are the amounts of money the company owes to others. Think of liabilities as obligations — the company has an obligation to make payments on loans or mortgages or they risk damage to their credit and business. Once all of the claims by outside companies and claims by shareholders are added up, they will always equal the total company assets. This transaction brings cash into the business and also creates a new liability called bank loan.
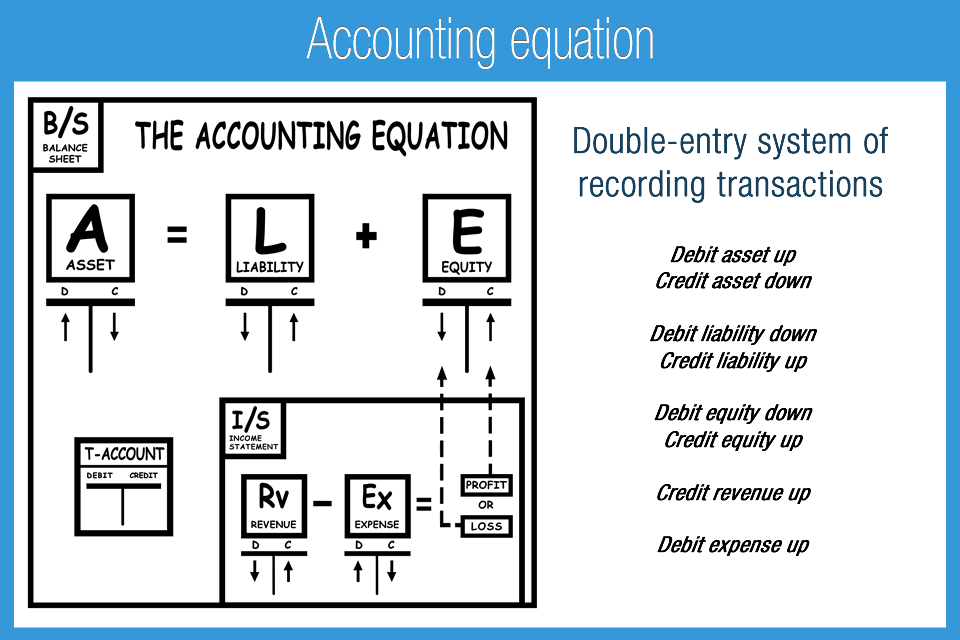
If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset). Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting. As its name implies, the Accounting Equation is the equation that explains the relationship of accounting transactions. The Accounting Equation states that assets equals the total of liabilities and equity. Whether you call it the accounting equation, the accounting formula, the balance sheet equation, the fundamental accounting equation, or the basic accounting equation, they all mean the same thing.
Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid. The accounting method under which revenues are recognized on the income statement when they are earned (rather than when the cash is received). The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity). Since the balance sheet is founded on the principles of the accounting equation, this equation can also be said to be responsible for estimating the net worth of an entire company. The fundamental components of the accounting equation include the calculation of both company holdings and company debts; thus, it allows owners to gauge the total value of a firm’s assets.
Taking time to learn the accounting equation and to recognise the dual aspect of every transaction will help you to understand the fundamentals of accounting. Whatever happens, the transaction will always result in the accounting equation balancing. The inventory (asset) of the business will increase by the $2,500 cost of the inventory and a trade payable (liability) will be recorded to represent the amount now owed to the supplier. In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash.

